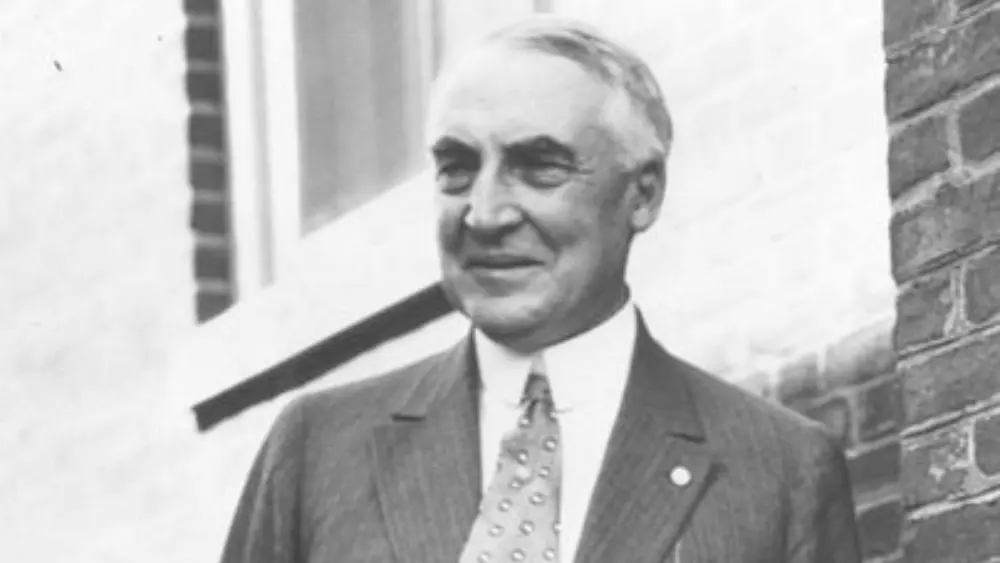
Warren G. Harding, the 29th President of the United States, made a lasting impact on the nation during the pivotal post-World War I period. Beyond his political tenure, Harding’s approach to military relations and foreign policy played a significant role in shaping the United States during a period of transition and global realignment.
Early Life and Political Ascent: The Journey to the Presidency
Warren G. Harding’s journey to the presidency was a testament to his steady political ascent and ability to navigate the complex landscape of American politics. Born into a modest upbringing on November 2, 1865, in Blooming Grove, Ohio, Harding’s early life instilled in him a sense of determination and a commitment to public service. His political career began at the local level, where he served in various capacities, including newspaper publisher and lieutenant governor of Ohio. Harding’s charisma, affable personality, and moderate political views endeared him to a broad spectrum of voters, paving the way for his rise through the political ranks.
Harding’s political ascent reached its zenith when, in 1920, he successfully secured the Republican nomination for the presidency. This pivotal moment marked a turning point in his career, propelling him into the national spotlight and setting the stage for the challenging road ahead. Capitalizing on a desire for a return to normalcy after the unruly years of World War I, Harding ran a successful campaign that emphasized his vision for a more stable and predictable America. His election as the 29th President marked the culmination of a remarkable journey, transitioning from a small-town upbringing to the highest office in the land. This ascent not only highlighted his personal achievements but also set the stage for his presidency during a critical period in American history. Moreover, it underscored the significance of his leadership role and the challenges that awaited him on the national stage.
Warren G. Harding: The Newspaper Publisher Turned Politician
Warren G. Harding’s transition from a newspaper publisher to a politician showcased his versatility and understanding of the intersection between media and public perception. Born on November 2, 1865, in Blooming Grove, Ohio, Harding began his career in the newspaper industry, eventually owning and operating the Marion Daily Star. Through his experience in journalism, he honed his communication skills and developed a keen awareness of the importance of shaping public opinion.
This background proved instrumental as Harding entered the political arena. His ability to articulate ideas and connect with diverse audiences set him apart, contributing to his political success. The skills acquired in the world of journalism played a crucial role in shaping Harding’s political persona, enabling him to effectively convey his messages and resonate with voters. This transition from a newspaper publisher to a seasoned politician marked a pivotal chapter in Harding’s life. Consequently, it significantly influenced his approach to leadership and communication during his subsequent tenure as the 29th President of the United States. This transformative shift not only shaped his political philosophy but also laid the groundwork for the challenges and opportunities that awaited him in the highest office in the land.
Foreign Policy and Military Relations: Navigating Post-War Realities
Warren G. Harding’s presidency was marked by the intricate task of navigating the post-war realities following World War I. Additionally, he faced the complex challenges of rebuilding a nation in the aftermath of global conflict. Moreover, his administration grappled with economic uncertainties and geopolitical shifts, further complicating the landscape. Elected in 1920, Harding inherited a world grappling with the aftermath of the global conflict and sought to chart a course for the United States in the changing international landscape. His foreign policy approach was rooted in a commitment to stability and a desire to move the nation beyond the turmoil of the war.
In shaping military relations, Harding prioritized a return to peacetime footing while recognizing the need for strategic considerations in a shifting global environment. His administration faced the challenge of demobilizing the military without compromising national security interests. Harding aimed to strike a balance between maintaining a capable defense and contributing to international efforts to prevent future conflicts. His diplomatic efforts and military policies reflected a pragmatic approach to the complexities of the post-war era, emphasizing stability, reconstruction, and a recalibration of America’s global role.
Warren G. Harding: Embracing Normalcy
Warren G. Harding’s foreign policy, often encapsulated by the slogan “Return to Normalcy,” was a deliberate effort to extricate the United States from the intense international engagements of the war era. Elected in the aftermath of World War I in 1920, Harding envisioned a return to a pre-war state of affairs characterized by reduced military commitments abroad and a focus on domestic priorities. The term “normalcy” conveyed his vision of a nation free from the exceptional circumstances of wartime, emphasizing stability and a return to familiar, peacetime conditions.
Under Harding’s leadership, the United States sought to disentangle itself from the complex web of international obligations and conflicts. This approach aligned with the sentiment of the American public, which was fatigued by the war and its aftermath. While “normalcy” became a rallying cry for domestic recovery and a return to pre-war routines, it also reflected Harding’s commitment to a measured and restrained foreign policy, emphasizing diplomatic solutions over military interventions and contributing to a period of relative calm in U.S. international relations during his presidency.
Veterans Affairs and Recognition: Honoring Those Who Served
Warren G. Harding’s presidency placed a significant emphasis on honoring and addressing the needs of Veterans, recognizing the sacrifices they made for their country during World War I. In an era marked by the aftermath of a devastating global conflict, Harding’s administration prioritized Veterans’ affairs as a key component of its agenda. Acknowledging the physical and psychological toll of war on returning soldiers, Harding sought to ensure that those who had served received the care and support they deserved.
Under Harding’s leadership, efforts were made to provide Veterans with the resources necessary for their reintegration into civilian life. This included initiatives to address healthcare needs, disability benefits, and vocational training programs. By focusing on Veterans’ affairs, Harding aimed to express the nation’s gratitude for their service while also recognizing the broader societal responsibility to care for those who had borne the burdens of wartime service. In doing so, he contributed to shaping a legacy of appreciation and support for America’s Veterans during a crucial period of recovery and transition for the nation.
Warren G. Harding: Commemorating Armistice Day
Warren G. Harding’s significant contribution to American history lies in his role in establishing Armistice Day, which later evolved into Veterans Day. The idea behind this national holiday was to commemorate the end of World War I and honor the brave people who had served in the military during that conflict. Harding recognized the importance of setting aside a day to express gratitude and remembrance for the sacrifices made by Veterans, acknowledging their dedication to preserving freedom and peace.
By signing the proclamation that designated November 11 as Armistice Day in 1926, Harding solidified a tradition that continues to this day. The transition to Veterans Day expanded the scope of recognition to encompass Veterans from all wars, emphasizing a broader appreciation for the service and sacrifices of military personnel. Harding’s initiative established a lasting national tradition that serves as a poignant reminder of the debt owed to those who have defended the nation in times of war.
Naval Disarmament and Diplomacy: The Washington Naval Conference
Warren G. Harding’s diplomatic endeavors during his presidency were highlighted by the convening of the Washington Naval Conference in 1921. In the aftermath of World War I, the global community was grappling with the need to prevent future conflicts and reduce the burgeoning arms race, particularly in naval forces. Recognizing the importance of international cooperation, Harding played a pivotal role in bringing together major naval powers, including the United States, the United Kingdom, Japan, France, and Italy, to negotiate and deliberate on naval disarmament.
The Washington Naval Conference resulted in a series of treaties, most notably the Five-Power Treaty, which aimed to limit naval construction and maintain a balance of naval power among the participating nations. The conference marked a significant diplomatic achievement in fostering dialogue and cooperation among major powers, setting a precedent for multilateral efforts to address global security challenges. Harding’s commitment to diplomatic solutions and disarmament reflected a desire to stabilize international relations and promote peace in the aftermath of a devastating world war.
Warren G. Harding: Architect of Naval Limitations
At the helm of the Washington Naval Conference in 1921, President Warren G. Harding emerged as the architect of significant naval limitations through key treaties, most notably the Five-Power Treaty. Recognizing the imperative to prevent an arms race and foster international cooperation, Harding engaged major naval powers, including the United States, the United Kingdom, Japan, France, and Italy, in negotiations to curb the growth of naval forces. The resulting treaties outlined specific limitations on naval construction, establishing a framework to maintain a balance of power at sea.
Harding’s role in these diplomatic endeavors showcased his commitment to stability and peace in the aftermath of World War I. By facilitating agreements that restricted the expansion of naval capabilities, he aimed to create an environment conducive to global security. The naval limitations negotiated under Harding’s leadership were a crucial step in reducing the potential for military escalation. Furthermore, beyond their immediate impact, these negotiations played a pivotal role in promoting international understanding during a crucial period in the post-war era. Additionally, they contributed to fostering diplomatic relations and laying the groundwork for collaborative efforts on a global scale. By fostering agreements on naval disarmament, Harding aimed to contribute to global stability and cultivate diplomatic relationships that would define the trajectory of international relations.
Legacy and Controversies: Assessing the Harding Presidency
Warren G. Harding’s presidency, though marked by notable achievements, is often remembered for the controversies that cast a shadow over his legacy. On the positive side, Harding’s foreign policy, known as the “Return to Normalcy,” sought to recalibrate the United States’ global engagement after the upheavals of World War I. He prioritized Veterans’ affairs, emphasizing the importance of supporting and honoring those who had served in the military. Additionally, Harding played a pivotal role in establishing Armistice Day, later renamed Veterans Day, as a national holiday to commemorate the sacrifices of Military Veterans.
However, the Harding administration became entangled in a series of scandals that marred its reputation. The most influential among these was the Teapot Dome scandal, which involved the illegal leasing of federal oil reserves. The revelations of corruption and misconduct eroded public trust in the government and left a stain on Harding’s legacy. While the president himself was not directly implicated in these scandals due to his untimely death in 1923, they significantly influenced historical assessments of his presidency. The complex legacy of Warren G. Harding encompasses both his contributions to national policies and the controversies that continue to shape perceptions of his time in office.

Warren G. Harding: The Teapot Dome Scandal
The Teapot Dome Scandal unfolded during Warren G. Harding’s presidency and, subsequently, remains one of the most notorious episodes in American political history. This scandal, which erupted into public consciousness, underscored the pervasive corruption that plagued the era. Moreover, it significantly tarnished Harding’s legacy, casting a long shadow over his administration. The scandal centered around the secret leasing of naval oil reserves, including the Teapot Dome in Wyoming, to private oil companies without competitive bidding. Albert B. Fall, Harding’s Secretary of the Interior, was at the center of the controversy, accepting bribes in exchange for these lucrative leases.
While there is no direct evidence linking Harding to the corruption, his administration faced severe criticism for inadequate oversight and the appearance of impropriety. Furthermore, these allegations cast a shadow over his presidency, raising questions about the effectiveness of governance and fostering public scrutiny during a critical period in American history. The scandal tarnished the reputation of Harding’s presidency and fueled public skepticism about the integrity of government officials. The Teapot Dome Scandal, alongside other instances of misconduct, played a significant role in shaping the narrative of Harding’s presidency, contributing to a mixed legacy that includes both accomplishments and the stain of corruption.