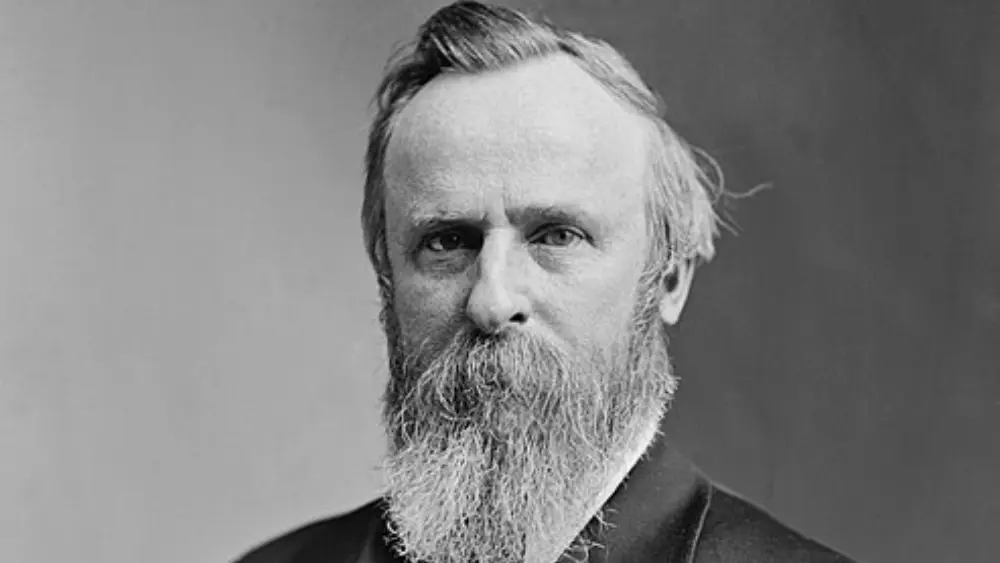
Rutherford B. Hayes, born on October 4, 1822, in Delaware, Ohio, was a key figure in American history. He served as the 19th President of the United States. Beyond his presidency, Hayes had a notable post-Civil War military career and political journey that left a lasting impact on the nation.
Early Life and Education: From Ohio to Harvard
Rutherford B. Hayes’s journey from Ohio to Harvard epitomized his dedication to education and laid the groundwork for a multifaceted career that would span law, military service, and political leadership. Growing up with a firm commitment to learning, Hayes pursued his higher education at Kenyon College, where he honed his intellectual skills and cultivated a passion for public service. His academic pursuits continued at Harvard Law School, where he deepened his understanding of legal principles, setting the stage for a career that seamlessly integrated legal expertise with a sense of civic duty.
Hayes’s educational background not only reflected his personal commitment to intellectual growth but also served as a solid foundation for the diverse roles he would undertake in the years to come. Moreover, the combination of academic rigor at Kenyon College and Harvard Law School played a pivotal role in shaping Hayes’s analytical abilities, legal acumen, and intellectual prowess that would characterize his later endeavors in law, military leadership, and, ultimately, his presidency. Consequently, this well-rounded education provided a multifaceted skill set that contributed significantly to his success in various fields of service.
Rutherford B. Hayes: Academic Excellence and Legal Prowess
Rutherford B. Hayes’s academic journey was marked by a trajectory of excellence and legal prowess. His educational pursuits, including studies at Kenyon College and Harvard Law School, laid the intellectual foundation for a distinguished career that seamlessly integrated legal expertise with a commitment to public service. Hayes’s academic achievements not only reflected his personal dedication to intellectual growth but also signaled a broader capacity for leadership and analytical thinking. Furthermore, these accomplishments served as a precursor to the remarkable contributions he would make in the legal and political arenas.
Having honed his legal skills at one of the nation’s most prestigious institutions, Hayes emerged from Harvard Law School with a comprehensive understanding of legal principles. This academic foundation would prove instrumental in navigating the complex landscapes of law, military leadership, and, ultimately, the presidency. Hayes’s commitment to academic excellence not only showcased his intellectual capabilities but also set the stage for a lifetime of public service and leadership. Moreover, this dedication made a lasting impact on American history, as he effectively transformed his scholarly work into a strong foundation for principled governance. Hayes’s journey from academic distinction to impactful leadership underscores the enduring influence of a strong educational foundation on the trajectory of a statesman’s legacy.
Civil War Service: Valor on the Battlefield
Rutherford B. Hayes’s response to the call of duty during the Civil War marked a pivotal chapter in his life. Setting aside his legal career, Hayes enlisted in the Union Army, demonstrating a deep commitment to the cause and a willingness to serve his country in a time of crisis. As he rose through the ranks, Hayes’s valor and leadership on the battlefield became increasingly evident. Consequently, his remarkable performance not only earned him the admiration and respect of both his fellow soldiers and superiors but also set the stage for a distinguished military career. Moreover, marked by unwavering dedication and strategic acumen, Hayes’s service in the military became a testament to his leadership capabilities and laid the groundwork for the impactful roles he would later undertake in the realms of law and politics.
Hayes’s contributions during the Civil War showcased not only his dedication to the Union cause but also his ability to lead under the most challenging circumstances. His acts of courage and strategic acumen in the heat of battle positioned him as a formidable military leader. This wartime experience would profoundly shape Hayes’s character and leadership style, thereby laying the groundwork for his future roles in public service and, eventually, the presidency. Consequently, the challenges and lessons from the battlefield became integral to his leadership philosophy, guiding his principled approach to governance and solidifying his commitment to service in the years to come.
Rutherford B. Hayes: Valor and Leadership in Battle
Rutherford B. Hayes’s role in the Civil War was characterized by extraordinary acts of valor and exemplary leadership on the battlefield. Enlisting in the Union Army and rising through the ranks, Hayes exhibited a deep sense of commitment to preserving the Union and upholding the values he held dear. His courage in the face of adversity and strategic acumen in various military engagements earned him a reputation as a distinguished officer. Consequently, he was not only respected by his peers but also garnered the admiration of his superiors. Hayes’s exemplary performance on the battlefield set the stage for a trajectory marked by leadership and the pursuit of excellence in diverse arenas of public service.
Hayes’s military service became a cornerstone of his legacy, shaping his character and instilling in him the values of duty and sacrifice. The experiences and lessons learned on the battlefield would influence his approach to leadership in subsequent roles, including his eventual presidency. Hayes’s unwavering commitment to the Union cause during the Civil War laid the foundation for a career marked by public service. Moreover, his deep sense of responsibility to the nation he had defended with valor became a guiding principle throughout his subsequent endeavors. Consequently, the values forged on the battlefield continued to resonate in his dedication to the well-being and progress of the United States, defining a trajectory characterized by principled leadership and a steadfast commitment to the common good.
Post-War Military Career: Transitioning from Soldier to Statesman
Post-Civil War, Rutherford B. Hayes confronted the significant challenge of transitioning from a distinguished military career to civilian life. The lessons learned on the battlefield, coupled with his unwavering dedication to public service, profoundly influenced his post-war trajectory. Hayes approached this transition with a commitment to continue contributing to the betterment of his nation, embodying the ethos of a soldier turned statesman.
In the aftermath of the war, Hayes leveraged the leadership skills honed on the battlefield to navigate the complex landscape of post-war reconstruction. His commitment to public service remained unwavering, and he sought avenues to contribute to the healing and rebuilding of the nation. This pivotal phase in Hayes’s life laid the groundwork for his subsequent entry into politics, where he would bring the same sense of duty, integrity, and strategic thinking that had defined his military service.
Rutherford B. Hayes: Navigating the Challenges of Reconstruction
Rutherford B. Hayes’s post-war military career was characterized by his active involvement in the intricate and challenging period of Reconstruction. Tasked with the responsibility of helping rebuild the nation after the Civil War, Hayes demonstrated leadership and commitment to the delicate process of healing. As a military officer, he played a crucial role in implementing Reconstruction policies that aimed to integrate the Southern states back into the Union, address issues of civil rights, and establish a foundation for a reunified and stronger nation.
Hayes’s approach to the challenges of Reconstruction reflected his commitment to fostering unity and reconciliation between the North and the South. His leadership during this critical period set the stage for his subsequent entry into politics, where he would continue to contribute to the nation’s healing and transformation. The experiences and lessons learned during the Reconstruction era profoundly influenced Hayes’s perspective on governance and justice, shaping his future role as a statesman dedicated to the principles of unity and equality.
Governor of Ohio: Political Ascent
Rutherford B. Hayes’s transition from the military to politics marked a seamless shift in his career. Elected as the Governor of Ohio, he swiftly applied the leadership qualities honed on the battlefield to the realm of governance. Hayes’s tenure as governor was characterized by a commitment to progressive policies and effective administration. His success in this role not only showcased his ability to navigate the complexities of state politics but also set the stage for broader political ambitions on the national stage.
As Governor of Ohio, Hayes implemented reforms in areas such as education and prison reform, earning a reputation for effective and principled leadership. His dedication to social justice and economic development resonated with constituents, laying the foundation for his future political endeavors. The success and impact of Hayes’s governorship positioned him as a rising political figure, leading to his eventual ascent to the presidency of the United States.
Rutherford B. Hayes: Progressive Policies and Economic Reforms
Rutherford B. Hayes’s tenure as the Governor of Ohio was characterized by a dedication to progressive policies and economic reforms. During his time in office, Hayes prioritized initiatives aimed at improving the lives of the state’s residents. Moreover, his commitment to public service manifested through a series of policies and programs designed to address the diverse needs of the community, showcasing a proactive approach to governance and a dedication to the well-being of the state’s population. His focus on social justice, education, and economic development demonstrated a commitment to addressing the pressing issues of his time.
One notable aspect of Hayes’s governorship was his advocacy for prison reform and improved treatment of mentally ill people. Recognizing the importance of humanitarian values in governance, he sought to create a more just and compassionate society. These progressive policies and reforms laid the groundwork for Hayes’s future leadership at the national level, as they reflected his overarching commitment to advancing the welfare of the American people.
Presidential Legacy: The Compromise of 1877 and Beyond
Rutherford B. Hayes’s presidency, which began in 1877, was shaped by the Compromise of 1877, a significant political arrangement that marked the end of the Reconstruction era. In the contentious election of 1876, Hayes faced Democrat Samuel Tilden in a disputed race where several Southern states submitted conflicting electoral votes. The Compromise of 1877 ultimately awarded Hayes the presidency in exchange for the withdrawal of federal troops from the South, effectively ending Reconstruction. While this compromise allowed Hayes to ascend to the highest office, it marked a complex and controversial chapter in American political history.
As president, Hayes pursued a conciliatory approach aimed at healing the divisions between the North and the South. He prioritized civil service reform, advocating for merit-based appointments and seeking to eliminate political patronage. Additionally, Hayes was committed to advancing education, particularly for African Americans in the South. Despite the challenges and controversies surrounding his election, Hayes’s presidency reflected a sincere and concerted effort to move the nation toward reconciliation and reform. This commitment was especially notable during a pivotal period in U.S. history, as he navigated the complexities of post-Civil War reconstruction and worked towards fostering a more inclusive and harmonious society.”
Rutherford B. Hayes: Civil Service Reform and Reconciliation
Rutherford B. Hayes, the 19th President of the United States, assumed office in 1877 with a firm commitment to civil service reform. Recognizing the pervasive issues of political patronage and corruption within the federal government, Hayes championed the merit-based selection of government officials. His push for civil service reform aimed to eliminate the prevalent spoils system, where government positions were distributed as rewards for political loyalty, and instead establish a system based on merit and competency. This endeavor laid the groundwork for subsequent reforms and set a precedent for the professionalization of the federal workforce.
Beyond civil service reform, Hayes sought to foster reconciliation and unity in a nation still grappling with the aftermath of the Civil War. Moreover, his efforts to bridge divides and heal wounds became crucial pillars of his presidency, contributing to a broader vision of national harmony and progress. The Compromise of 1877, which led to his contested election victory, involved an agreement to withdraw federal troops from the South, effectively ending Reconstruction. Hayes, recognizing the need for healing, pursued policies aimed at easing tensions between the North and the South. While his presidency was relatively short-lived, his emphasis on civil service reform and reconciliation contributed significantly to a broader shift in American governance. Consequently, this pivotal focus set the stage for future administrative reforms, leaving a lasting impact on the trajectory of governmental practices and shaping the course of subsequent administrations.

Post-Presidential Life: Advocacy and Legacy
Post-presidential life for Rutherford B. Hayes was characterized by continued advocacy for causes close to his heart. He remained a steadfast proponent of education, believing in its transformative power for individuals and society. Hayes’s commitment to civil service reform also persisted, consistently reflecting his enduring belief in the importance of ethical governance. Moreover, this steadfast dedication underscored his legacy as a principled leader. It also advocated for transparency and accountability in public service throughout his distinguished career. Beyond his personal advocacy, the Hayes legacy endures through the institutions he fervently championed. The Hayes Presidential Library and Museums, dedicated to preserving his papers and artifacts, stand as a testament to his contributions to American history. These institutions serve as educational resources, allowing future generations to engage with the ideals and principles that defined Hayes’s public service.
In addition to leaving an institutional legacy, Hayes’s impact resonates in the broader narrative of American governance. His emphasis on civil service reform paved the way for subsequent administrations to address issues of corruption and political patronage. As a leader who sought reconciliation and unity in the aftermath of the Civil War, Hayes played a crucial role in shaping the nation’s path toward healing. His commitment to principles of ethical governance and educational advancement leaves an enduring mark on the fabric of American history, reflecting a legacy that extends far beyond his time in the presidency.