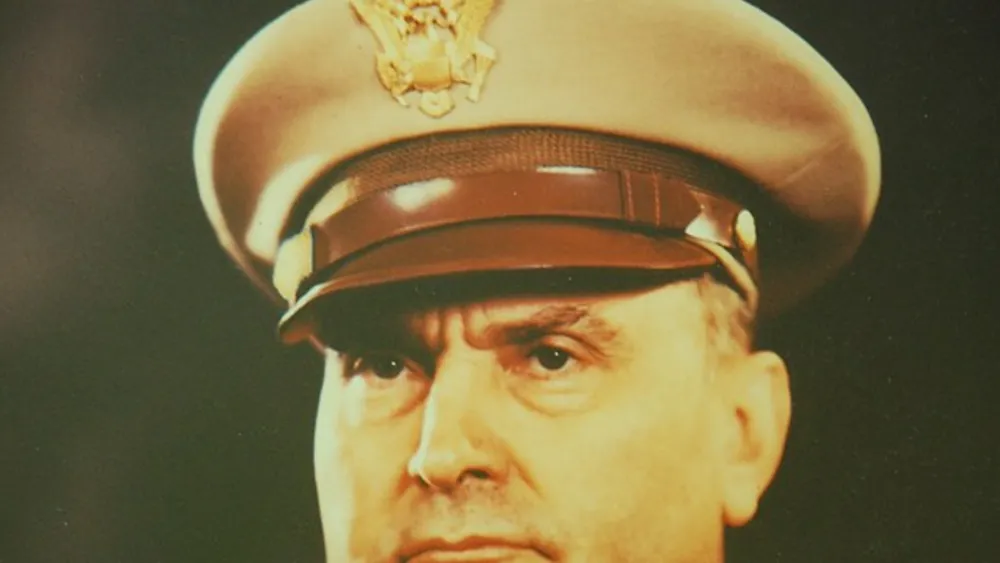
Ira Clarence Eaker might not be as well-known as other prominent figures in aviation history. Born on April 13, 1896. In Field Creek, Texas, Ira C. Eaker rose through the ranks to become a key architect of the United States Air Force.
His journey from a small Texas town to the highest echelons of military leadership is a testament to his dedication to aviation and exceptional contributions to the field.
Eaker’s early fascination with aviation, sparked by witnessing the Wright brothers’ aircraft in 1913, set the stage for a remarkable career. His decision to join the United States Army Signal Corps during World War I began a lifelong commitment to military aviation and innovation.
As he earned his pilot’s wings in 1918, Eaker’s career took flight. He rapidly became a respected aviator and instructor, guiding the next generation of pilots into the skies.
Ira Eaker and the Dawn of Aviation Technology
Ira Eaker’s fascination with aviation began at an early age. His passion was ignited during a momentous event in 1913 when he attended a demonstration of the Wright brothers’ aircraft. The awe-inspiring sight of these early flying machines soaring through the sky left a lasting impression on his young mind, setting him toward the skies.
Despite his early interest in aviation, Eaker initially pursued a degree in engineering at the University of Texas. However, his passion for flying never waned. When the United States entered World War I, he seized the opportunity to contribute to the war effort.
He decided to join the United States Army Signal Corps, a pivotal moment that would shape his destiny.
In 1918, Ira Eaker earned his pilot’s wings, joining the ranks of those pioneering the uncharted skies. This was an era of rapid advancement in aviation technology. Eaker found himself at the forefront of these exciting developments.
Like many of his generation, he witnessed firsthand the transformative changes that were taking place in the field of aviation.
World War II and the Strategic Bombing Campaign
Ira Eaker’s most significant contributions to military aviation and strategic thinking came during World War II. In 1942, he was promoted to Major General and tasked with leading the Eighth Air Force, the largest and most powerful strategic bomber force in Europe.
It was in this role that he made his mark on history.
Eaker believed in the power of strategic bombing and the importance of daylight precision bombing. He knew that to win the war in Europe, the United States needed to establish air supremacy. Under his leadership, the Eighth Air Force executed a relentless campaign against German targets. It included factories, transportation hubs, and oil refineries. This strategy aimed to cripple the German war machine and disrupt its ability to wage war effectively.
The “Combined Bomber Offensive” plan, which Eaker played a crucial role in developing, was a coordinated effort between the Eighth Air Force and the Royal Air Force (RAF). It involved massive daylight bombing raids. With the Eighth Air Force flying deep into enemy territory and the RAF conducting nighttime bombing missions.
The goal was to weaken the German war effort and support the Allied ground forces.
Weakening the German War Machine
Eaker’s leadership and dedication to precision bombing were pivotal elements in the success of the strategic bombing campaign during World War II. As the head of the Eighth Air Force, he set the tone for the precision and accuracy required for daylight bombing raids over enemy territory.
His meticulous planning and emphasis on hitting specific military and industrial targets played a vital role in weakening the German war machine.
However, what truly set Ira Eaker apart was his commitment to ethical warfare. Even during the most intense and high-stakes air campaigns, he prioritized the well-being of civilians in the target areas.
This dedication to minimizing civilian casualties reflected his moral compass. Furthermore, he demonstrated a deep sense of responsibility. Eaker’s approach not only showcased the military effectiveness of precision bombing but also underscored the principles of honor and humanity in the heat of battle.
His legacy as a military leader who strived for both victory and ethical conduct continues to inspire those who study the history of warfare.
Founding the U.S. Air Force Academy
Following World War II, Ira C. Eaker continued to contribute to developing the United States Air Force. He was important to the founding of the United States. He is also a great influence on the establishment of the Air Force Academy and the Strategic Air Command (SAC). Eaker had a bigger picture than his immediate wartime responsibilities. So, he recognized the importance of having a strong and effective air force in the long run.
Eaker retired from the Air Force in 1947 but remained active in various advisory roles within the defense community. He authored books on air power and continued to influence the development of military strategy.
His contributions to the formation and growth of the U.S. Air Force were immeasurable. Moreover, he was a steadfast advocate for the importance of airpower in modern warfare.

Ira Eaker and His Legacy in Military History
Though Ira C. Eaker passed away on August 6, 1987, his legacy remains alive and well in the annals of military history. His contributions to military aviation and the United States Air Force continue to reverberate through time.
His commitment to the strategic application of airpower and his dedication to the principles of precision bombing are not mere historical footnotes. It became an enduring lesson for contemporary and future generations.
Military historians and scholars continue to study and admire Eaker’s strategic acumen, his ethical approach to warfare, and his innovative thinking in the field of aviation. His ideas and leadership serve as a source of inspiration. Therefore, it provided invaluable insights into the evolution of modern military strategy.
In conclusion, Ira C. Eaker, a nameless celebrated by some of his contemporaries, remains a foundational figure in military aviation.
His life and career are a powerful reminder of the enduring impact that one individual can have on history, leaving a legacy that transcends time.